Table of Content
Home Owners’ Loan Corporation; Provided mortgage assistance to homeowners or would-be homeowners by providing them money or refinancing mortgages. In the end, more than 800,000 homeowners repaid the HOLC credit, but a majority were able to repay them before the due date. This is in contrast to interest-only loans during the 1920s when the borrower made payments of the same amount as the amount of interest every month until the expiration of the loan, and then pay the principle at the conclusion the term of loan. Before the 1930s, loan the borrower would usually pay the principal due by borrowing new loans.
The HOLC was attempting to keep from selling too many homes too quickly in order to prevent negative impacts on prices of housing. This is also in contrast to loans offered by Building and Loans (B&L) in the 1920s, which typically ran between 10 and 12 years. HOLC is often cited as the originator of mortgage redlining, although, this claim has also been disputed.
Did the HOLC refinanced mortgages?
HOLC ended its operations officially in the year 1951, when its assets were transferred for private lending. Direct reduction loans have been the most frequent kind in American mortgage. Moreso, it helped financial institutions pay off their depositors or investors as necessary and to remain in business. It also saved the local governments from the disastrous effects of widespread unemployment and loss of income.
The HOLC stopped its lending activities in June, 1936, by the terms of the Home Owners' Loan Act. The historian David Kennedy did not exaggerate in claiming that the HOLC and the housing legislation it set in motion "revolutionized the way Americans lived." Diminished wages, widespread unemployment, and few, if any, refinancing options made it difficult for home owners to meet monthly mortgage payments during the Great Depression.
HOLC
The success of this sympathetic outreach was best demonstrated by the fact that the foreclosure rate for HOLC's risky mortgages was no greater than that for much safer mortgages accepted by banks and insurance companies. The Roosevelt administration credited the HOLC with a restoration of economic morale, a reduction of foreclosure rates, and payment of almost $250 million in delinquent taxes to state and municipal governments. Subsequent scholars have generally agreed with this positive evaluation, asserting that the HOLC was significant because it introduced the long-term, self-amortizing mortgage.
As intended, the main beneficiaries were homeowners at the lower end of the middle class with incomes in the $50 to $150 monthly range, persons who in the private market would have lost their homes. The Home Owners’ Loan Corporation was a federal program established in 1933 to provide relief to troubled mortgage borrowers and their lenders. The Home Owners’ Loan Corporation operated by purchasing mortgages from private lenders and issuing new mortgages to the borrowers.
What effects did the Great Depression have on the credit industry?
In 1939, the company lowered rates to 4 1/2 per cent for a wide range of the borrowers. The HOLC loans typically amortized which meant that they would have equal monthly payments each month for the loan. It offered money at 5 percent, provided insurance for its loans through the Federal Housing Authority and the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation, and allowed up to twenty-five years for repayment. Every loan situation was handled individually, including personal visits to prevent default.

It tended to wait until the borrower had failed to make payments on the loan for more than a year before it foreclosed on the loan. The HOLC tried to avoid selling too many homes quickly to avoid having negative effects on housing prices. Ultimately, more than 800,000 people repaid their HOLC loans, and many repaid them on time. HOLC officially ceased operations in 1951, when its last assets were sold to private lenders.
It was formed out of the strong desire of the then president to help refinance debts and bring solutions. Just like every other laon system, Home Owners Loan Corporation has a structured system in which it operates. On June 13, 1933, President Roosevelt signed the Home Owners’ Loan Act into law. During this period, HOLC made over 1 million loans totaling about $3.1 billion – $575 million of which went to individuals . Roosevelt asked Congress on April 13, 1933, for "legislation to protect small home owners from foreclosure." Lawmakers responded by creating the Home Owners Loan Corporation on June 13, 1933.
HOLC was established as an emergency agency under Federal Home Loan Bank Board supervision by the Home Owners' Loan Act of 1933, June 13, 1933. It was transferred with FHLBB and its components to the Federal Loan Agency by Reorganization Plan No. It was assigned with other components of abolished FHLBB to the Federal Home Loan Bank Administration , National Housing Agency, by EO 9070, February 24, 1942. Its board of directors was abolished by Reorganization Plan No. 3 of 1947, effective July 27, 1947, and HOLC was assigned, for purposes of liquidation, to the Home Loan Bank Board within the Housing and Home Finance Agency. It was terminated by order of Home Loan Bank Board Secretary, effective February 3, 1954, pursuant to an act of June 30, 1953 (67Stat.121). Since Kenneth T. Jackson's work in the 1980s, scholars have increasingly portrayed HOLC as a key promoter of redlining and a driver of racial residential segregation and racial wealth inequality in the United States.
The HOLC was established pursuant to theHome Owners' Loan Corporation Act. In June 1933, the Home Owners' Loan Act, following the president's lead, sailed through Congress. The law authorized $200 million to set up the Home Owners' Loan Corporation with authority to issue $2 billion in tax-exempt bonds. The money raised would enable the HOLC to rescue imperiled mortgages by offering financing up to 80 percent of assessed value, to a maximum of $14,000. There followed a rush to file applications in 1934 by those holding 40 percent of all mortgaged properties, of which half with lowest risk were accepted.

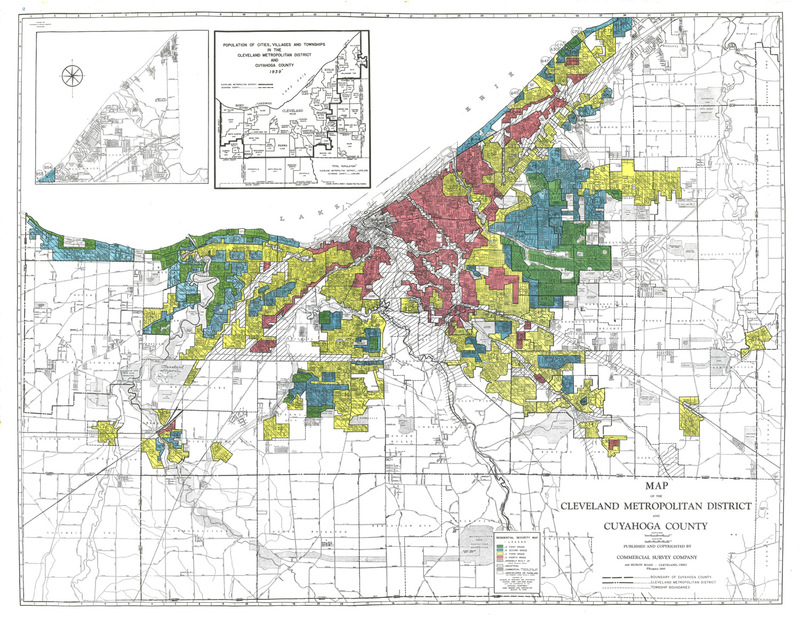
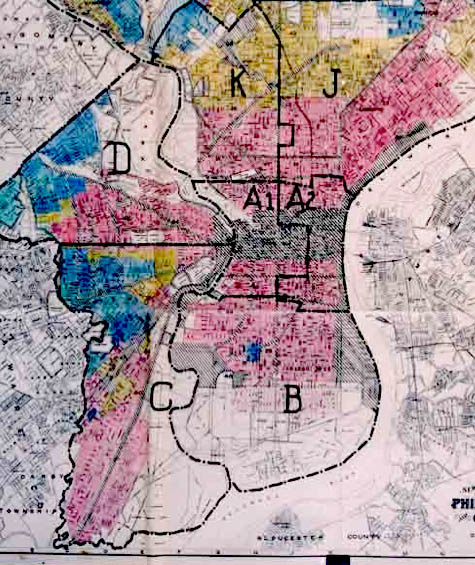
It is now expected that when the HOLC is fully liquidated, the Treasury will have been repaid its capital advance in full, plus a surplus of several million dollars. It was formed to improve home ownership by insuring loans so lenders can offer lower down payments, lower closing costs, and make credit qualifying easier. Home Owners' Loan Corporation HOLC. Helped home-owners and mortgage companies. Government payed companies for the home-owners so they could keep their homes and pay off w/ lower interest and longer time. 1935 Created for both industrial recovery and for unemployment relief. During the late 1930s, the Home Owners' Loan Corporation developed a series of area descriptions with color-coded maps of cities that summarized mortgage lending risk.
These maps document how loan officers, appraisers and real estate professionals evaluated mortgage lending risk during the era immediately before the surge of suburbanization in the 1950’s. Neighborhoods considered high risk or “Hazardous” were often “redlined” by lending institutions, denying them access to capital investment which could improve the housing and economic opportunity of residents. Between 1933 and 1935, the HOLC made slightly more than one million loans. At that point it stopped making new loans and then focused on the repayments of the loans. The typical borrower whose loan was refinanced by the HOLC was more than 2 years behind on payments of the loan and more than 2 years behind on making tax payments on the property. The HOLC eventually foreclosed on 20 percent of the loans that it refinanced.
“Type D” neighborhoods were outlined in red and were considered the most risky for mortgage support. Specifically, the chapter compares how two federal lending programs—the Home Owners' Loan Corporation and the Federal Housing Administration —carried out their respective missions, and their long-term consequences for metropolitan America. The typical borrower who that was refinanced by HOLC was more than two years behind in the repayments of the loan, and more than two years behind in paying taxes for the home. In the wake of the publication of Kenneth T. Jackson’s work in the 1980s, researchers have been increasingly portraying HOLC as a major driver of redlining and as an agent of racial segregation as well as racial wealth inequality across the United States. Buyers and borrowers couldn’t meet mortgage payments due to a high increase in unemployment and income reductions.

No comments:
Post a Comment